Leg Length Discrepancy (LLD)
What is Leg length discrepancy?
Leg length discrepancy is a condition where one leg is longer than the other. It is a pretty common problem, because the two halves of a human body are never perfectly symmetrical.
What causes leg length discrepancy?
The causes are many and they may be of three kinds:
- congenital disorders (hemihypertrophy, dysplasias, vascular disorders, hypoplastic limbs, one limb significantly shorter)
- acquired disorders (infections, traumas, neurological diseases, …)
- tumors
What are leg length discrepancy symptoms?
A slight difference in lower limbs length may be asymptomatic, while a significant difference can cause an evident limp and other difficulties in running and playing.
The difference in leg length can range from less than 1 cm up to 10 cm. according to its pathogenesis (causes).
The greater the difference is the more the symptoms and signs show up
Common symptoms include:
- posture related problems (pseudo scoliosis)
- walking problems (limping, toe-walking, …)
- back pain
Leg length discrepancy measurement and diagnosis?
During a physical examination a doctor observes the child while he/she sits, stands and walks and can measure discrepancy when the child is laying barefoot.
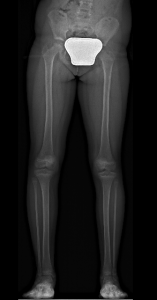
To get a more precise measurement the doctor may order long full legs standing X-ray.
Leg length discrepancy treatments
Treatments may vary depending on:
- The size of the discrepancy
- Child’s age
- The cause of the discrepancy
There is a widespread belief that leg length discrepancy may be damaging to the spine or the hip, but this assumption is not supported by any data. It is proven instead that a discrepancy up to 1.2 cm does not have evident effects.
It is important to keep track of the leg growth and progression of LLD and to formulate a strategy based on the patient’s age and speed of increased LLD.
Nonsurgical Treatments
Literature suggests that individuals with a minor limb length discrepancy (less than 1.2 cm) usually do not require any treatments.
Among nonsurgical treatments there are:
- Observation: if the child has not yet reached skeletal maturity.
- Shoe lift
Surgical Treatment
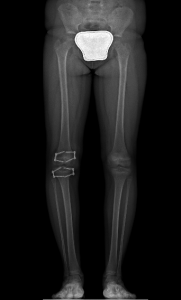
In still-growing children, if the discrepancy is expected to be more than 3 cm it is possible to equalize the length of the legs with a relatively simple surgery.
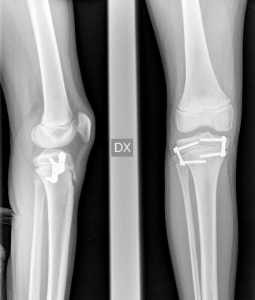
Epiphysiodesis (Temporary Epiphysiodesis)
Surgery is performed on day hospital basis and it has the purpose of slowing the growth of the longer limb (asymmetrical growth). The result is not immediate, but the difference between the legs gradually decreases during growth. This surgery must be performed before the child’s growth is completed.
Limb Lengthening
There is another more invasive surgery, that may be performed to lengthen the shorter limb especially when differences are minor than 3-4 cm or at skeletal maturity
The doctor cuts the bone in the shorter leg into two segment to apply an “external fixator” to the leg that must be manually lengthened each day by the patients of a family member (Ilizarov Technique)
About Professor Portinaro’s experience
Prof. Portinaro is one of the most qualified pediatric orthopedic surgeons in the world for leg and foot diseases and treatments.
He examined more than 3000 patients performed more than 1000 surgeries for both shortening or lengthening techniques.
Prof. Portinaro has also a huge experience in treating neurological diseases such as cerebral palsy or vascular malformations that may have leg length discrepancy as possible consequence.
