Anterior Cruciate Ligament ACL injury
About ACL injury
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments to to provide stability of the joint in the anteroposterior plane in the knee and ACL injury is one of the most common knee damages.
Where is the ACL located?
The knee joint is made of three bones: femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap). Bones are connected by ligaments and in the knee there are four main ligaments:
- Collateral ligaments (Lateral and medial on the two side of the knee)
- Cruciate ligaments (Anterior and Posterior, crossed inside knee joint)

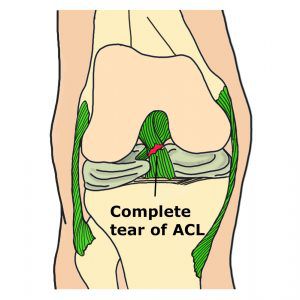
ACL injury occurs when the ligament sprain or tear.
 There are three types or grades of sprain, depending on the severity of the injury.
There are three types or grades of sprain, depending on the severity of the injury.
- Grade 1 refers to a mild damage. The ligament has been stretched but the joint is still stable
- Grade 2 It is also referred to as partial tear of the ligament and occurs when the ligament becomes loose.
- Grade 3 or complete tear of the ligament occurs when the ligament is split into two pieces and as a consequence of that the knee joint is unstable.
ACL tear symptoms
The typical symptom of ACL injury is the feeling of “popping” noise or sensation in the knee.
Other signs and symptoms may include:
- Severe pain
- Swelling (within a few hours)
- Loss of full range of motion
- A feeling of instability in the knee
Anterior Cruciate Ligament injury causes
Most ACL injuries occurs during sport activities that put frequent stress on the knee with movement such as rapid change of direction, sudden slowing down, jumping, direct contact. Football, basketball, soccer, gymnastic are sports with the highest rate of ACL injury.
Other risk factor may be
- Age. Teenagers are usually most active so the are at higher risk
- Sex. Female are five to eight times more likely than boys to tear their ACL.
ACL injury Diagnosis
During a physical examination the orthopedic surgeon will test the child’s knee checking all its structures. A physical exam may be enough to make the diagnosis finding anteroposterior instability with specific tests (Lachman test, anterior drawer test, jerk test).
Anyway the doctor may order other tests such as:
- X-ray to exclude a bone fracture
- Magnetic resonance imaging. ACL MRI offers an image of all the soft tissue in the knee and allows to show the severity of the injury or to check for other damages
ACL injury treatments
First-aid care is fundamental to reduce pain and swelling.
Rest, ice, compression and elevation (R.I.C.E. model of self-care) are the most recommended things to do immediately after a suspected injury to the knee.
A torn ligament doesn’t heal without surgery.
Nonsurgical treatment is preferred in older patients that have very limited activity.
In this case treatment may include bracing and physical therapy
ACL Surgery
Surgery may be recommended if:
- the patient is a children or young adults
- the patients is an athlete or has an intense sport activity
- more the one ligament is injured
- the injury cause the knee to buckle frequently
The most common surgery for ACL injury is ACL reconstruction.
The orthopedic surgeon replace the damaged ligament with a tissue graft. It means that he uses a piece of tendons from another part of the knee (usually from hamstring tendons at the back of the thigh).
After surgery, fast and intensive rehabilitation will play a vital role. It may take from 5 to 8 weeks before an athlete can return to sport activity if muscle strength is fully restored.
