Flat Foot
What is Flat feet?
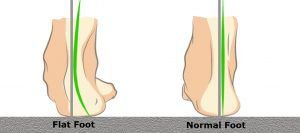 Flat feet, also known as Pes Planus or Fallen Arches, constitutes the main reason of pediatric orthopedic requested consultation.
Flat feet, also known as Pes Planus or Fallen Arches, constitutes the main reason of pediatric orthopedic requested consultation.
Flat foot is a condition in which the the medial or internal arch of the foot shrinks or totally disappears.
The foot is naturally flat in children and usually children with flat foot start developing an arch in their early years of life.
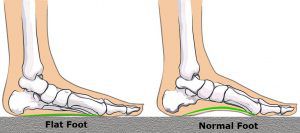 This attitude is considered physiological up to 8/10 years. After that, as children grow, the arches of the feet gradually shapes. This process ends up to 10/12 years of age.
This attitude is considered physiological up to 8/10 years. After that, as children grow, the arches of the feet gradually shapes. This process ends up to 10/12 years of age.
Flat foot can be flexible or rigid
Symptoms of flat feet
Most children have no particular symptoms but sometimes they may experience foot pain in the heel and arch area. Pain may worsen during activity and is more frequently associated with rigid flat foot.
 What causes “Flexible” Flat foot?
What causes “Flexible” Flat foot?
A defective development of the foot arch may have different causes:
- congenital abnormalities of the foot bones
- muscular insufficiency of the arch or foot muscle
- neuromuscular pathologies
- ligamentous hyper laxity or generalized ligamentous laxity (loose ligaments).
What causes “rigid” flat foot?
Rigid flat foot is usually due to a malformation of the bone called “coalition”. That means that the bones are not separated and a bone and a bone or cartilage bar keep them united.
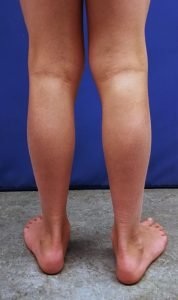
How is Flat foot diagnosed?
The orthopedic surgeon must examine the child to decide whether treatment is needed.
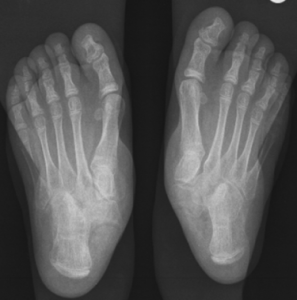
In children with flat foot, the arch of the feet disappear when standing.
To diagnose the problem, the children are asked to stand on their toes. If the arch reappears the flat foot is called flexible and no more tests or treatments are necessary.
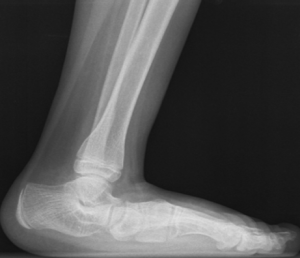
If the arch does not form with toe-standing (rigid flat feet), or if there is pain, other tests may be needed, such as X-rays.
How Flat Foot is treated
Nonsurgical treatments
The orthopedic surgeon decides whether to start treatment or adopt an observation strategy. If flat foot don’t cause pain, no treatment is necessary.
If flatfeet is painful the orthopedic might suggest the best orthotics for flat feet (medical devices such as flat feet insoles and arch supports for flat feet)
Anyway the use of arch supports has always been a controversial issue.
Other treatments may include:
- shoes for flat feet (The orthopedic may suggest the best shoes and running shoes for flat feet)
- Physical therapy for runners. (To improve the way the child run in order to reduce the risk of overuse injuries)
Flat feet surgery
Only around 10-12 years surgical treatments should be taken into account in particular if symptoms include feet pain or arch pain while standing and according to radiological picture.
How Prof. Portinaro treats Flat Foot
Prof. Portinaro is one of the most qualified surgeons for foot diseases and their treatments.
In his long-running career he has been treating flat feet with a surgical approach examining more than 1000 feet each year.
Then, since flat feet is the commonest foot condition, Prof. Portinaro performed more than 10,000 flat feet surgeries in his career
Prof. Portinaro and his team perform a minimally invasive surgery that consists in placing a screw right below the ankle (tarsus). The screw is fixed to the heel sinus tarsi and prevents the rear foot to rotate inward.
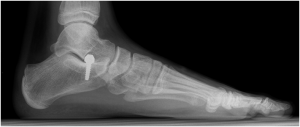
The operation is performed in day surgery and patients undergo moderate sedation with local anesthesia. Just a couple of hours after surgery patients can fully weight-bear during the immediate postoperative period.
There’s no need to use casts, while the use of crutches for a few days ensures safe ambulation.
Surgeries are never risk free (infections, hematomas, etc.) but complications are rarely observed and resolved with excellent results. Usually, the screw inside the foot is not removed, unless important functional requirements come up in adulthood.

 What causes “Flexible” Flat foot?
What causes “Flexible” Flat foot?